Synchronizing Eye-Tracking Data with EEG Using Gazepoint
Eye-tracking technology is a powerful tool in research, and Gazepoint provides a user-friendly solution for capturing precise gaze data. However, in many studies, it’s necessary to synchronize eye-tracking data with other physiological measurements, such as EEG (electroencephalogram), to gain deeper insights. Fortunately, Gazepoint makes this process straightforward.
To synchronize Gazepoint’s eye-tracking data with EEG, it’s often easiest to run both systems on the same computer, provided that the machine has enough processing power. This allows the data from both devices to be captured in parallel. Gazepoint provides a USER data field within its API that can be utilized for synchronization. For instance, you can send a specific marker—such as “EEG_START”—into the USER data field at the moment EEG data collection begins.
By exporting the data to CSV format from Gazepoint Analysis, you can identify the time point where the “EEG_START” marker appears in the eye-tracking data stream. This timestamp can then be used to align the eye-tracking data with the corresponding EEG data, ensuring that both streams are perfectly synchronized for further analysis.
The Gazepoint system supports a range of programming languages for the API, including MATLAB, C++, and Python, making it versatile and easily adaptable for custom research setups.
This integration opens up new possibilities for multimodal research, combining eye-tracking with EEG to study cognitive processes, attention, and more in greater depth.
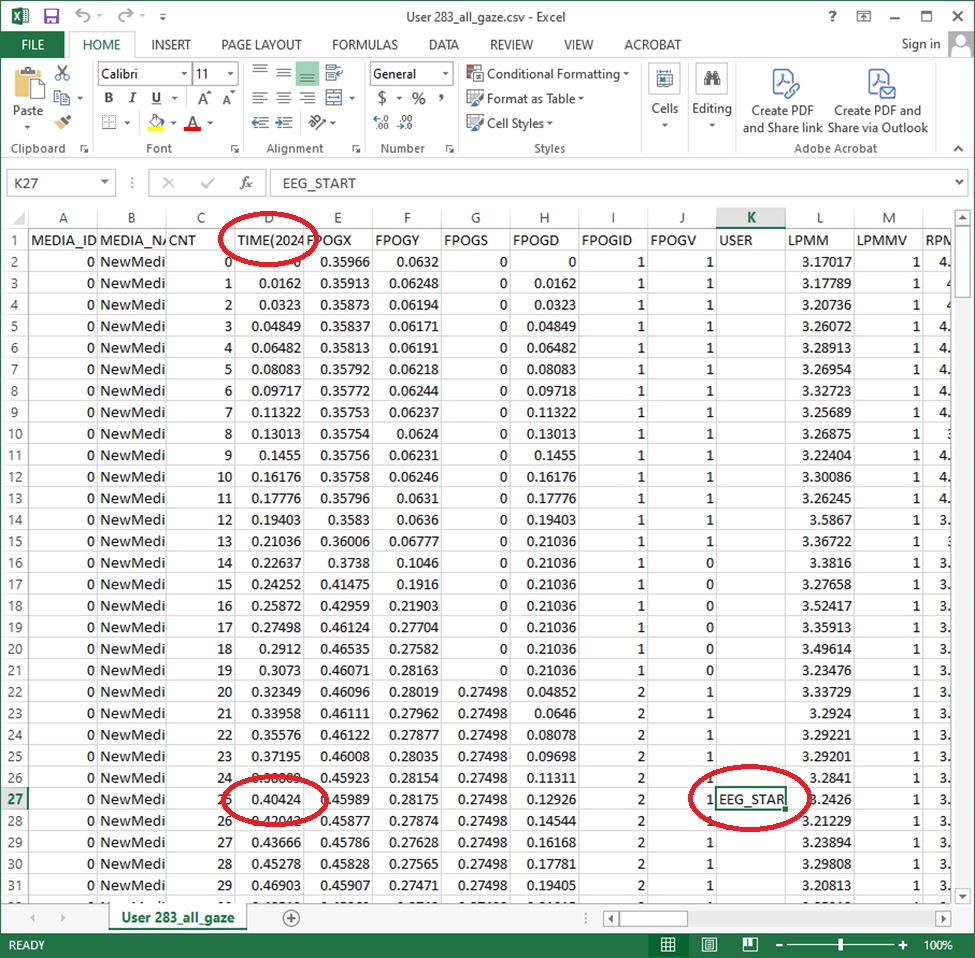
In the eye-tracking data snapshot shown above, the EEG_START string was sent to the USER field at 0.40424 seconds (from the TIME column). In the header of the TIME column the computer date and time at which the recording began (TIME = 0 seconds) is listed as TIME(2024/09/23 19:38:41.899). In this example the start of the EEG data recording occurred 0.40424 seconds after the time listed in the header.